Most companies today have several options on hand for saving their files. Traditionally, you’d store your files on an external thumb drive, hard disk, or other medium. Of course, the downside to using these methods is that you need to keep the storage medium on hand to access your files. This isn’t always convenient, as they can easily get lost or stolen. Moreover, it becomes almost impossible to share these files with your colleagues or friends, unless you plan on e-mailing them copies every time.
Make sure you’re getting the most out of your SharePoint by checking out our top 5 permissions best practices.
Nowadays, cloud solutions allow us to store our files on centralized servers and access them from a multitude of devices. Two cloud-based platforms that allow you to save, share, and sync files across devices are Microsoft’s SharePoint and OneDrive for Business. In this article, we’ll evaluate the key differences between these two document management systems to see which is better for your business.
SharePoint
SharePoint is a document sharing and storage platform that lets users collaborate on files, documents, and projects. Equipped with an impressive range of document libraries, task lists, calendars, workflows, wikis, and other features, SharePoint helps team members collaborate through a team-oriented platform. Information is available to all members, and anyone with proper access privileges can modify and create documents.
SharePoint has three deployment modes: on-premises, cloud, and hybrid. Each mode comes with a comprehensive set of pricing models, making SharePoint ideal for businesses of all sizes.
Pros
- Central repository—SharePoint offers a single, convenient record management system for storing and sharing company files.
- Collaboration—SharePoint was designed specifically as team collaboration software. It offers tools like Docs, Excel, Tasks, Calendar, and Workflow, as well as Outlook integration capabilities to improve communication and help keep employees connected.
- Flexibility—SharePoint provides countless options for integration and customization. You can implement it with the help of your IT team to meet your company’s requirements.
- Versatility—SharePoint offers a variety of features and works well with other company systems (CRM/ERP).
- Security—Microsoft has greatly improved the authentication and authorization protocols for SharePoint to allow for fully customized user access. This means you can specify various access privileges to restrict what your team members can view. Even users who are fairly proficient in changing access levels will struggle to get where they don’t belong thanks to the improvements that have been made in this area.
- Scalability—SharePoint is extremely scalable and can address multiple business requirements in one package, saving you money, time, and IT resources.
- Integration—SharePoint integrates well with most other software. If you use SharePoint for your business solutions, you can still access documents from other applications in SharePoint, such as Microsoft Office.
- Reputation—SharePoint is a billion-dollar product in Microsoft’s lineup. It’s extremely well adopted both globally and locally, with plenty of vendors in this space to support you.
- Integrated reports – Generate documents that can be integrated with Power BI.
Cons
- Pricing—SharePoint is an expensive solution. If an enterprise chooses the traditional on-premise intranet option, then the initial cost of infrastructure, license, and customization is going to be quite high. However, the long-term improvements in workflow fully justify the price.
- Setup—you need the right expertise to set it up correctly. This means you may need to consult IT specialists who are more familiar with the software.
- Training—SharePoint requires a lot of configuration and training to train users.
- Rollout time—SharePoint takes a long time to adopt and properly roll out in a company.
- Reliance on browsers—if there’s no internet access, there’s no SharePoint.
- Incompatible with small environments—unfortunately, it’s not feasible to deploy SharePoint in small environments because of the cost of licensing and training.
OneDrive for Business
With OneDrive, you can store your files on the cloud and access them by simply signing in to your account from any device that has a local OneDrive folder, the app, or an internet connection. Your files are automatically synced for your convenience, and you can edit or update them at any time.
For clarity, it’s worth noting that there are two versions of OneDrive: OneDrive Personal and OneDrive for Business. Though these two share the same name, they don’t offer the exact same features. We’ll mainly focus on OneDrive for Business in this article, but we’ll briefly note the differences between the two below.
OneDrive Personal (often simply referred to as OneDrive) lets you store personal files such as family photos, favorites, and other documents on the cloud through a single account that you own. What you do with these files and how you store them is entirely up to you—you can share them with people you trust or simply keep them all private.
In contrast, OneDrive for Business is a business-oriented online storage system that lets you manage project documents and collaborate with your colleagues. Your OneDrive for Business account is managed by your organization—that is, the site collection administrators of your company can control what you do.
Pros
- Functionality – A large number of employees access their work files out of the office in ways that make IT departments shudder. Whether it is via personal emails, DropBox, Google Docs or good old fashioned flash drives. By integrating OneDrive for Business, employees can keep the same functionalities but within boundaries pre-set out by IT.
- Document backup – With OneDrive for Business, files that would usually be saved to a folder on a user’s work desktop or laptop can now be stored via cloud storage instead. This is a great approach because if an organization loses access to a device, their files can still be easily accessed. Downtime in this case can be kept to a minimum.
- Simple synchronization – Backing up documents online is not just a security measure, it is also a great mobility feature. When users save files locally in a synchronized folder, these documents are then saved automatically to their OneDrive folder. This means users can easily access their documents from anywhere.
- Co-authoring feature – Collaborate on files with other people at the same time by syncing the files with Office. If there is a conflict between file versions users can decide if they want to merge, change, or keep both copies of the document.
- File preservation – This feature allows organizations to preserve OneDrive files once an Office 365 account is deleted. The default settings will keep the data for 30 days, but administrators can set their own timeline, with 3560 days (ten years) being the maximum amount of time.
- External sharing – This is a very popular feature of Office 365 storage services. You can choose from one of the following four sharing options:
- Completely disable external sharing
- Only existing external users can access the services
- Files and sites can be shared with new and existing users
- Anyone, including anonymous users, can access the files without logging in
Want tips on how to master OneDrive for Business? Check out our blog 14 OneDrive for Business Configurations You Need to Use
Cons
- External sharing – Yes, this is both a pro and a con. External sharing is great for enabling collaboration, but the fact that any user can access files without logging in increases the chances of confidential data loss. A company could mitigate this risk by integrating other products such as Azure Rights Management and Windows InTune, but it is still safer to use a sharing option that requires a user to sign-in.
- Document management – As it is not intended as a place to permanently store records, there are no management features such as auditing, or reporting.
- Storage – By default OneDrive for Business only gives each user 1TB of storage. However, depending on what plan you are on, it is possible to pay for more, with a maximum storage allowance of 5TB.
Feature Summary: SharePoint vs OneDrive for Business
Below, we’ve compiled a convenient chart to help you better understand the differences between SharePoint and OneDrive for Business.
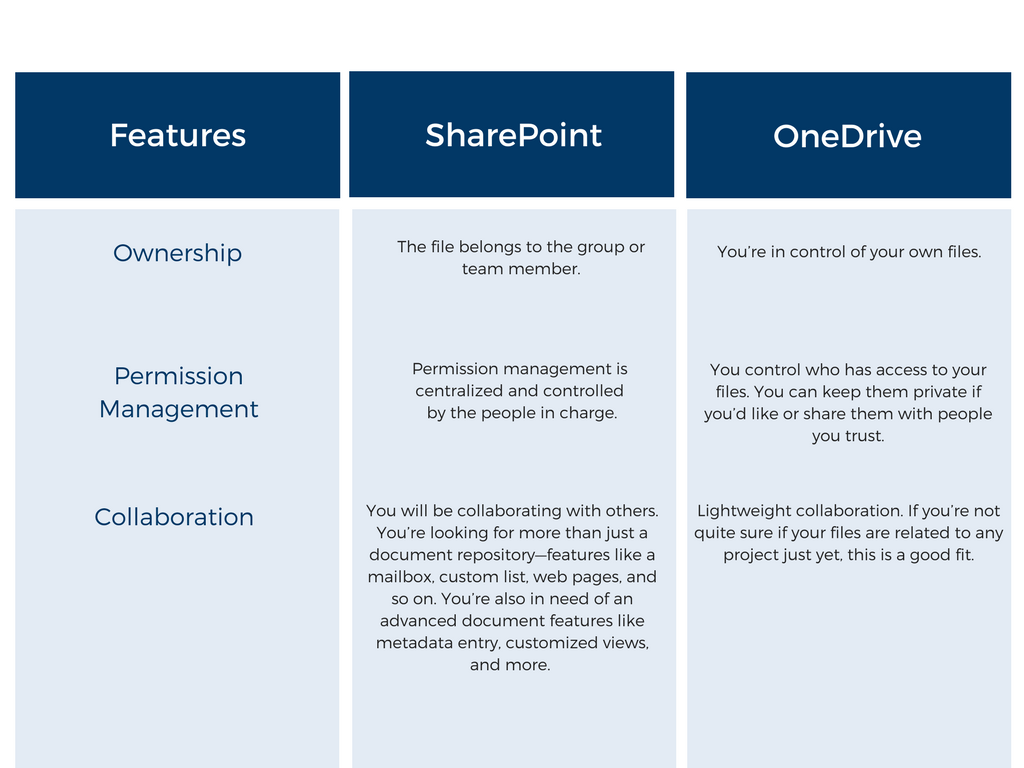

If you’re looking for collaborative document management system for your business, SharePoint is the ideal solution. It offers a number of integrated apps and productivity tools to help your team members collaborate, stay in touch, and coordinate their tasks. Overall, SharePoint is a robust platform for enterprise content management. Use SharePoint for the “we” part of your work, especially if you require more advanced content management.